SUMMARY
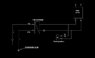
The discussion focuses on calculating the total cooling effect in Watts from a heat pump system with a Thermal Heat Rejection (THR) value of 154 kW. The heat pump's evaporator operates at temperatures of 5°C in and 0.5°C out, with a flow rate of 6.2 l/s. The cooling battery, which functions as a thermal storage element, is designed for temperatures of 7°C to 12°C and requires a flow rate of 3.87 l/s to produce 72 kW. The participants clarify the flow direction and the need for additional valves to optimize the system's performance.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Thermal Heat Rejection (THR) in heat pump systems
- Knowledge of flow rates and temperature differentials in HVAC systems
- Familiarity with cooling batteries and their role in air handling units
- Basic principles of fluid dynamics as applied to thermal systems
NEXT STEPS
- Research the calculation methods for cooling capacity in heat pump systems
- Learn about the design and operation of cooling batteries in HVAC applications
- Investigate the use of valves for flow balancing in thermal systems
- Explore the impact of temperature differentials on heat pump efficiency
USEFUL FOR
Engineers, HVAC technicians, and system designers looking to optimize heat pump performance and cooling efficiency in thermal management systems.