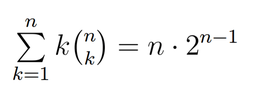SUMMARY
The equality in question arises from the binomial theorem, specifically the identity $\sum_{k=0}^n\binom{n}{k}=2^n$. This identity can be understood through combinatorial proofs, which count the number of subsets of a set of size $n$. Each element in the set has two choices: to be included in a subset or not, leading to a total of $2^n$ subsets. Various proof techniques exist, including induction and differentiation, which further validate this equality.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of binomial coefficients, specifically $\binom{n}{k}$
- Familiarity with the binomial theorem and its applications
- Basic combinatorial concepts, including subsets and counting principles
- Knowledge of proof techniques such as induction and differentiation
NEXT STEPS
- Study the binomial theorem and its implications in combinatorics
- Explore combinatorial proofs and their applications in mathematics
- Learn about induction as a proof technique in mathematical reasoning
- Investigate differentiation methods used in proving mathematical identities
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, students of combinatorics, and anyone interested in understanding the foundations of the binomial theorem and its proofs.