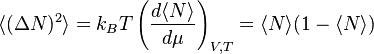SUMMARY
The variance in particle number, denoted as \(\langle (\Delta N)^2 \rangle\), is derived using the Fermi-Dirac distribution and the grand-canonical partition function. The mean particle number \(\langle N \rangle\) is expressed as \(\langle N \rangle = k_B T \frac{1}{Z} \frac{dZ}{d \mu}\), where \(Z\) is the grand-canonical partition function. The second moment \(\langle N^2 \rangle\) is similarly derived as \(\langle N^2 \rangle = (k_B T)^2 \frac{1}{Z} \frac{d^2 Z}{d \mu^2}\). These equations are valid under constant volume and temperature conditions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Fermi-Dirac statistics
- Knowledge of grand-canonical partition function
- Familiarity with Gibbs factors and their significance
- Basic concepts of statistical mechanics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Fermi-Dirac distribution in detail
- Learn about the grand-canonical ensemble and its applications
- Explore the concept of Gibbs factors in statistical mechanics
- Investigate the implications of variance in quantum statistical systems
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, statisticians, and researchers in quantum mechanics or statistical mechanics who are interested in the behavior of particle systems and their statistical properties.