Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the limit of the expression \( e^{\tan(x)} \) as \( x \) approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2} \) from the right. Participants explore the behavior of the tangent function near this point and its implications for the limit of the exponential function.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
- One participant initiates the discussion by questioning how to approach the limit of \( e^{\tan(x)} \) as \( x \) approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2}^{+} \).
- Another participant suggests first considering the limit of \( \tan(x) \) as \( x \) approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2}^{+} \).
- Participants note that \( \tan(\frac{\pi}{2}) \) approaches \( -\infty \) from the right side, prompting further inquiry into the behavior of \( e \) raised to this power.
- It is proposed that since \( \lim_{x\to-\infty} e^x = 0 \), the limit of \( e^{\tan(x)} \) as \( x \) approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2}^{+} \) would also be 0.
- Another participant reinforces this by stating that \( e^{\tan(x)} \) can be expressed as \( \frac{1}{e^{|\tan(x)|}} \) over the interval \( \left(\frac{\pi}{2}, \pi\right] \), leading to the same conclusion of the limit being 0.
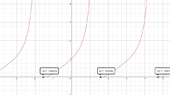
- There is a mention of the graphical behavior of the tangent function as it approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2} \), indicating that it tends to \( -\infty \) and thus supports the conclusion regarding the limit of the exponential function.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree that the limit of \( e^{\tan(x)} \) as \( x \) approaches \( \frac{\pi}{2}^{+} \) is 0, based on the behavior of the tangent function. However, the discussion includes various approaches and confirmations of this conclusion without explicit consensus on the method of derivation.
Contextual Notes
Some participants provide additional insights into the graphical representation of the tangent function and its limits, which may not be fully explored or resolved in the discussion.