SUMMARY
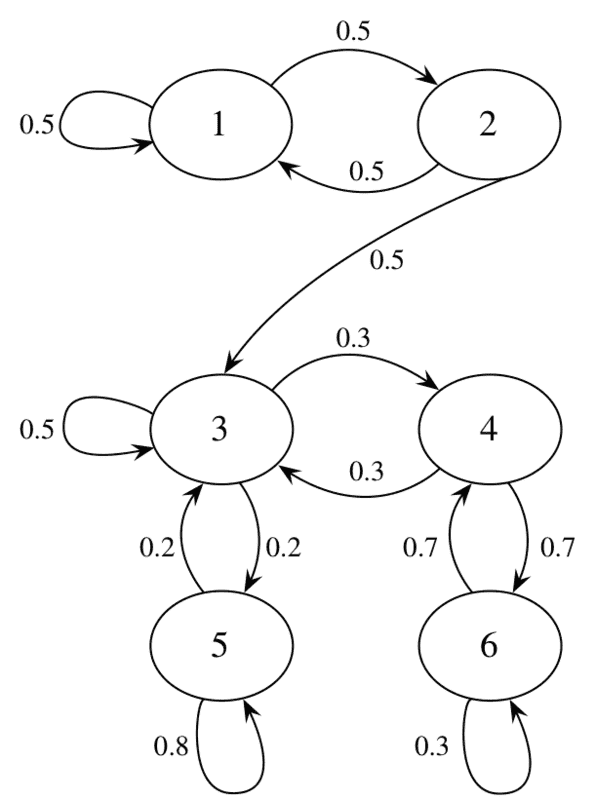
The discussion focuses on analyzing a Markov chain defined on the state set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} for a programming project. The transition matrix is a 6 x 6 sparse matrix, and the long-term behavior is determined by evaluating the limit of the matrix raised to the power of n as n approaches infinity. The distribution of returns to state 1 follows a geometric distribution with a parameter of 1/4, and the key question is to determine the fraction of time the chain spends in state 3.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Markov chains and their properties
- Familiarity with transition matrices and their applications
- Knowledge of geometric distributions in probability theory
- Ability to compute limits of matrix powers
NEXT STEPS
- Study the construction and properties of transition matrices in Markov chains
- Learn how to compute the long-term behavior of Markov chains using matrix exponentiation
- Explore the concept of stationary distributions in Markov processes
- Investigate the implications of geometric distributions in stochastic processes
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, computer science, and data science who are working on projects involving Markov chains and stochastic modeling.