Discussion Overview
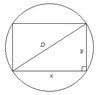
The discussion revolves around determining the dimensions of a rectangular beam that can be cut from a cylindrical trunk with a given diameter "D" and length "L". The focus is on maximizing the volume of the beam, considering the geometric constraints of the circular cross-section of the trunk.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Exploratory
Main Points Raised
- One participant inquires about the dimensions of a rectangular beam that maximizes volume from a cylindrical trunk.
- Another participant suggests that the problem involves maximizing the area of a rectangle inscribed within a circle and prompts for the constraints and objective function.
- A subsequent reply proposes that the optimal shape of the beam is a square with a side length of D/2, maintaining that the length of the beam equals the length of the trunk.
- Further contributions clarify the objective function as the area of the rectangle, expressed as A(x,y) = xy, and introduce the constraint based on the Pythagorean theorem: x² + y² = D².
- One participant indicates they derived a relationship leading to y = x = D/sqrt(2) as part of the maximization process.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants present multiple approaches to the problem, with some agreeing on the use of inscribed rectangles and others proposing specific dimensions. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the optimal dimensions and the derivation process.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not fully resolved the mathematical steps involved in maximizing the area or volume, and assumptions about the relationships between the dimensions and the constraints are still being explored.