SUMMARY
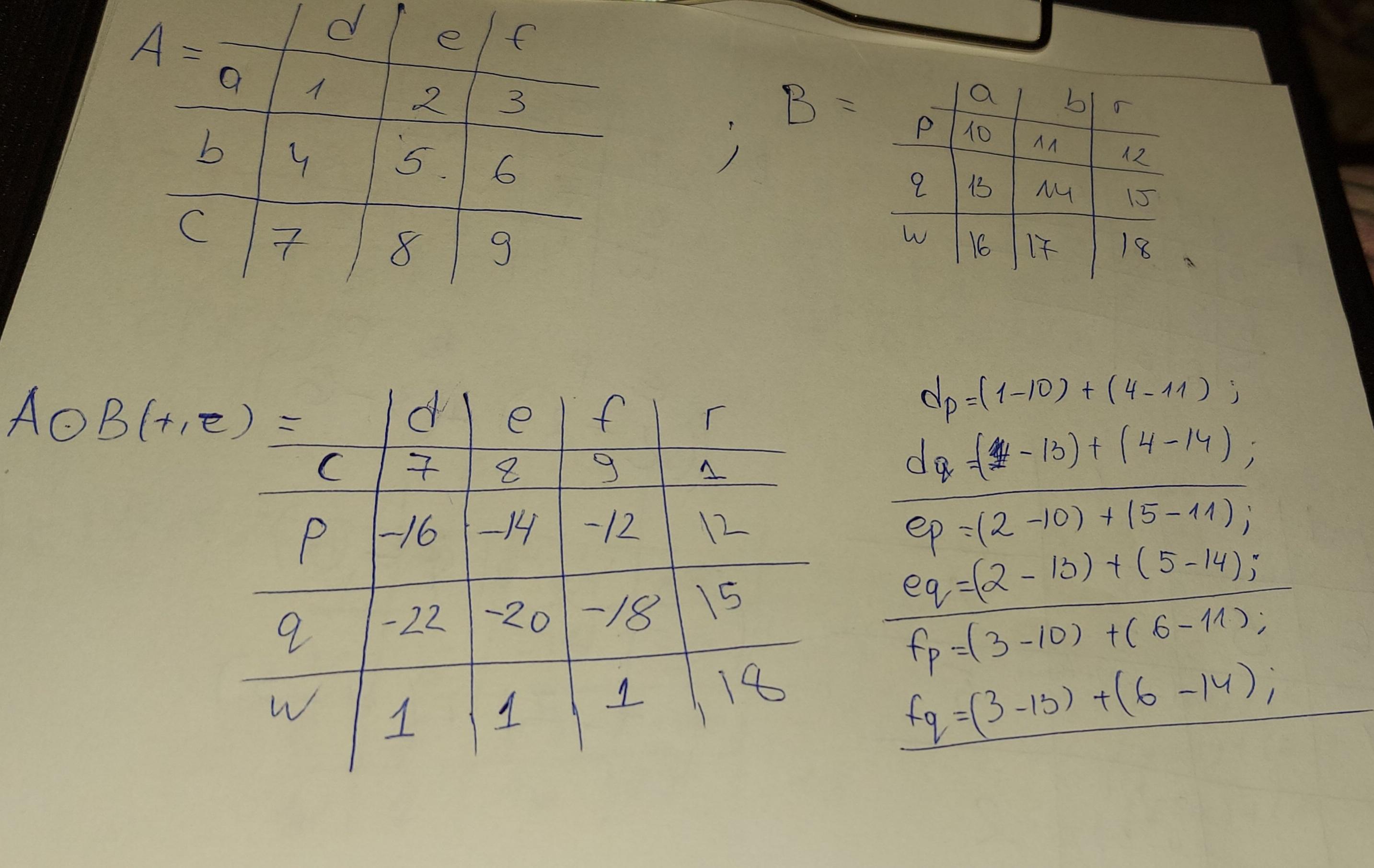
This discussion focuses on the multiplication of indexed matrices, specifically the matrices A and B defined as A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3\\ 4 & 5 & 6 \\7 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} and B = \begin{pmatrix}10 & 11 & 12 \\ 13 & 14 & 15 \\ 16 & 17 & 18 \end{pmatrix}. The method for calculating the product AB involves taking the dot product of rows from matrix A with columns from matrix B. The first row of the resulting matrix AB is calculated as \begin{pmatrix}84 & 90 & 96\end{pmatrix}, with further calculations required for the remaining rows.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of matrix notation and operations
- Knowledge of vector dot products
- Familiarity with indexed matrices
- Basic linear algebra concepts
NEXT STEPS
- Study matrix multiplication techniques in linear algebra
- Learn about vector dot products and their applications
- Explore indexed matrices and their uses in computational problems
- Review examples of matrix multiplication with different dimensions
USEFUL FOR
Students, mathematicians, and computer scientists interested in linear algebra, particularly those working with matrix operations and computational algorithms.