- #1
PhysicsKT
- 17
- 0
Homework Statement
A honeybee is flying parallel to tabletop at height
2. The attempt at a solution
Let us work in the frame moving with the constant velocity
The solution of this equation would be at
My question is: is this wrong? The answer matches, but an acquaintance comes and asks me, why did you assume linear acceleration? Why do you think honeybee only wants to travel the least distance? Because the problem says: find the minimum time...
Please help me asap.
Attachments
-
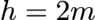 c1975b3ac41216fc73cd36b0e4434cf67a5bcf30.png574 bytes · Views: 522
c1975b3ac41216fc73cd36b0e4434cf67a5bcf30.png574 bytes · Views: 522 -
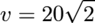 9ad7fa55a37ab127b0ffc739f278c0c65e1bb490.png829 bytes · Views: 528
9ad7fa55a37ab127b0ffc739f278c0c65e1bb490.png829 bytes · Views: 528 -
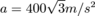 e207f7dd1f98225ce817d245322a4dce995d73f3.png1.2 KB · Views: 517
e207f7dd1f98225ce817d245322a4dce995d73f3.png1.2 KB · Views: 517 -
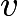 a9f23bf124b6b2b2a993eb313c72e678664ac74a.png286 bytes · Views: 301
a9f23bf124b6b2b2a993eb313c72e678664ac74a.png286 bytes · Views: 301 -
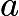 c7d457e388298246adb06c587bccd419ea67f7e8.png286 bytes · Views: 316
c7d457e388298246adb06c587bccd419ea67f7e8.png286 bytes · Views: 316 -
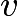 a9f23bf124b6b2b2a993eb313c72e678664ac74a.png286 bytes · Views: 316
a9f23bf124b6b2b2a993eb313c72e678664ac74a.png286 bytes · Views: 316 -
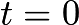 5a607fd61885c014512c949fee18869690330407.png427 bytes · Views: 324
5a607fd61885c014512c949fee18869690330407.png427 bytes · Views: 324 -
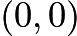 f9603ca3089464e548fc6f1366bc474e7efef8d9.png605 bytes · Views: 318
f9603ca3089464e548fc6f1366bc474e7efef8d9.png605 bytes · Views: 318 -
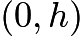 57acd195dfc44927ca230fbd512bf32cfeba669c.png685 bytes · Views: 318
57acd195dfc44927ca230fbd512bf32cfeba669c.png685 bytes · Views: 318 -
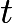 e0d2bf360290fd61d1c1557e763f2622363b3d35.png251 bytes · Views: 300
e0d2bf360290fd61d1c1557e763f2622363b3d35.png251 bytes · Views: 300 -
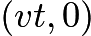 461eaa0c47244a9b94b69aa8936ba22b85973cd6.png742 bytes · Views: 313
461eaa0c47244a9b94b69aa8936ba22b85973cd6.png742 bytes · Views: 313 -
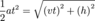 19ad84175ba436ee089e05012a8eb9b9e98c8515.png1.6 KB · Views: 297
19ad84175ba436ee089e05012a8eb9b9e98c8515.png1.6 KB · Views: 297 -
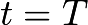 65360f557164b60bd01f1b1122adc6ff987ba117.png423 bytes · Views: 309
65360f557164b60bd01f1b1122adc6ff987ba117.png423 bytes · Views: 309 -
 aafa64c95c85226b146a31ab1462091f6a82a19e.png2.6 KB · Views: 300
aafa64c95c85226b146a31ab1462091f6a82a19e.png2.6 KB · Views: 300