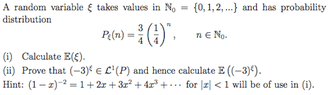Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating expected values in probability, specifically dealing with a discrete probability distribution function (p.d.f.) involving a variable n. Participants explore the mathematical steps involved in deriving the expected value and address confusion regarding the application of a series formula.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents a p.d.f. and attempts to calculate the expected value E{ξ} using a series formula, leading to a proposed result of 1/3.
- Another participant questions the calculation, suggesting that the numerator should be 1/4 instead of 3/4 when applying the series formula.
- A later reply indicates that the mistake in the calculation has been corrected, but does not clarify the nature of the correction.
- Participants express gratitude for the assistance provided in resolving the confusion.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
The discussion contains disagreement regarding the correct application of the series formula and the resulting expected value. The confusion about the numerator indicates that the participants have not reached a consensus on this point.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved mathematical steps and assumptions regarding the application of the series formula, particularly in relation to the numerator in the expected value calculation.