Question about Quantum dot (picture)
Click For Summary
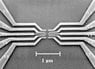
This discussion centers on the significance of a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image depicting a double quantum dot (QD) structure. The image illustrates gate lines (V1, V2) that apply voltage potentials to define the quantum dots, fabricated on a III-V semiconductor like Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). The discussion highlights the creation of a quasi-2D electron gas (2DEG) beneath the surface, where electrons are confined in the XY plane due to the applied gate voltage, forming the quantum dots. Applications of quantum dots include use in detectors and potential advancements in technology such as quantum dot-based displays.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
- Familiarity with III-V semiconductors, particularly Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
- Knowledge of quantum dots and their applications
- Basic principles of electron gas behavior in semiconductor physics
- Research the properties and applications of Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) in semiconductor technology
- Learn about the fabrication techniques for quantum dots and their integration in electronic devices
- Study the behavior of quasi-2D electron gases (2DEG) and their significance in quantum mechanics
- Explore advancements in quantum dot technology, including potential applications in displays and detectors
This discussion is beneficial for physicists, materials scientists, and engineers involved in semiconductor research, as well as anyone interested in the applications of quantum dots in modern technology.
Similar threads
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 5 ·