SUMMARY
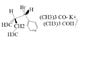
The discussion focuses on determining the stereochemistry of a reaction product involving two stereocenters, specifically identifying configurations as R or S. The reaction is identified as an E1 elimination due to the use of potassium t-butoxide, a strong base, in a polar solvent (t-butanol). The presence of an allylic bromine suggests that the reaction will favor a carbocation mechanism, as the C-Br bond can break to form a resonance-stabilized carbocation. The final stereochemical configurations of the product can be one of R,R; R,S; S,R; or S,S.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of stereochemistry, including R and S configurations.
- Knowledge of elimination reactions, specifically E1 and E2 mechanisms.
- Familiarity with the role of solvents in reaction mechanisms, particularly polar solvents.
- Basic concepts of carbocation stability and resonance.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mechanisms of E1 and E2 eliminations in organic chemistry.
- Learn about stereochemical representation using wedge and dash notation.
- Explore the effects of solvent polarity on reaction mechanisms.
- Investigate the stability of carbocations and the factors influencing their formation.
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, organic chemists, and anyone studying reaction mechanisms and stereochemistry in organic reactions.