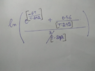
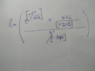
Solve ln(a/b+1) Using Identity ln(a+b)=ln b + ln(a/b+1)
- Context: Undergrad
- Thread starter Gurasees
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Logarithm
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on solving the expression "ln(a/b+1)" using the identity "ln(a+b)=ln b + ln(a/b+1)". Participants emphasize that the expression cannot be simplified further without a specific equation to solve for T. Numerical methods and power series expansions are recommended for approximating solutions, particularly for the expression involving T, which is dependent on the interval of convergence for the logarithmic and exponential functions.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of natural logarithms and their properties
- Familiarity with exponential functions and their power series expansions
- Basic knowledge of numerical methods for solving equations
- Concept of interval of convergence in series expansions
- Learn about power series expansions for exponential and logarithmic functions
- Research numerical approximation techniques for solving equations
- Study the properties of logarithmic identities and their applications
- Explore the use of Wolfram Alpha for solving complex mathematical expressions
Mathematicians, students studying calculus, and anyone interested in solving logarithmic and exponential equations numerically.
Similar threads
- · Replies 1 ·
Undergrad
Integrating 1/x with units (logarithm)
- · Replies 15 ·
High School
Issue With Algebra of Logarithms
- · Replies 8 ·
Undergrad
Universal Gravity without Shell Theorem
- · Replies 13 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 5 ·