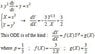SUMMARY
The discussion centers on solving the ordinary differential equation (ODE) of the form \( \frac{dY}{dX} = f(X)Y^p + g(X) \) with specific parameters: \( p = \frac{1}{3} \), \( f(x) = -\frac{3}{2}x \), and \( g(x) = \frac{2}{3} \). Participants noted that while the Bernoulli ODE can be solved analytically, this particular case does not yield an analytical solution when \( g(x) \) is a non-zero constant. Consequently, a numerical method is required to find a solution.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
- Familiarity with Bernoulli ODEs
- Knowledge of numerical methods for solving differential equations
- Basic algebraic manipulation skills
NEXT STEPS
- Research numerical methods for solving ODEs, such as the Runge-Kutta method
- Study the characteristics of Bernoulli ODEs and their solutions
- Explore software tools for numerical analysis, such as MATLAB or Python's SciPy library
- Learn about the implications of non-integer powers in differential equations
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, students studying differential equations, and professionals involved in numerical analysis or mathematical modeling will benefit from this discussion.