Matt H
- 7
- 0
The diagram shows a straight wire carrying a flow of electrons out of the page. The wire is between the poles of the permanent magnet. The direction of the magnetic force exerted on the wire is:
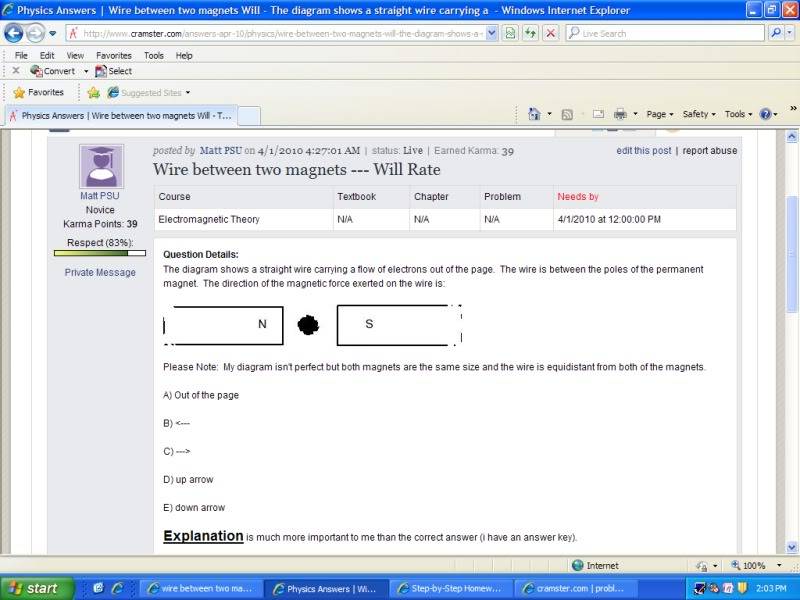
Please Note: My diagram isn't perfect but both magnets are the same size and the wire is equidistant from both of the magnets.
A) Out of the page
B) <---
C) --->
D) up arrow
E) down arrow
An explanation is much more important to me than the correct answer (i have an answer key).
Please Note: My diagram isn't perfect but both magnets are the same size and the wire is equidistant from both of the magnets.
A) Out of the page
B) <---
C) --->
D) up arrow
E) down arrow
An explanation is much more important to me than the correct answer (i have an answer key).