- #1
Emilijo
- 36
- 0
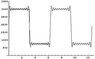
In Fourier series we have small waves on the top of big waves (the function seems like that),
but the small waves do not have the same amplitude. Does somebody know how to get a function with waves and small waves on the top but with the same amplitude.
but the small waves do not have the same amplitude. Does somebody know how to get a function with waves and small waves on the top but with the same amplitude.