Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the energy emitted by black holes, particularly in relation to their mass and the mechanisms involved, such as Hawking radiation and other processes. Participants explore theoretical frameworks, mathematical formulations, and implications of black hole thermodynamics.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant inquires about the energy output of black holes relative to their mass, seeking a percentage of mass converted to energy per second.
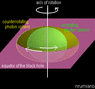
- Another participant references Hawking radiation, explaining that as particles escape, a black hole loses energy and mass, and provides a formula for estimating power emitted by a nonrotating black hole.
- A later reply notes that smaller black holes radiate more quickly than larger ones, but their lifespans are extremely long, potentially on the order of the age of the universe.
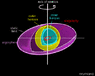
- One participant introduces the idea that rotating black holes can lose energy through processes like the Penrose process and superradiance, suggesting that up to 29% of a black hole's mass can be extracted through these means.
- Another participant discusses the implications of rotation on Hawking radiation, positing that a maximal Kerr black hole may not emit radiation at all.
- Further contributions explore the concept of naked singularities and the stability of black holes, referencing theoretical work by notable physicists and discussing the conditions under which these phenomena may occur.
- Participants also engage in mathematical discussions regarding the equations governing black hole horizons and their translation between different units.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is no consensus on the exact mechanisms and implications of energy loss in black holes, with multiple competing views and interpretations presented throughout the discussion.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference various equations and theoretical models, indicating a reliance on specific assumptions and definitions that may not be universally accepted or resolved within the discussion.