SUMMARY
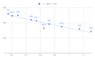
The discussion centers on calculating the speed of sound using the relationship between frequency and wavelength, specifically through the equation V = F * λ. The user initially inquired about finding the speed of sound by calculating the area under a frequency vs. time graph, which was corrected to a frequency vs. wavelength graph. After performing a definite integral, the user obtained a speed of sound measurement of 223.03 meters/second, which was questioned for its accuracy. The conversation emphasizes the importance of dimensional analysis in verifying the correctness of equations used in physics.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the wave equation V = F * λ
- Basic knowledge of dimensional analysis in physics
- Familiarity with graphing frequency and wavelength data
- Experience with definite integrals and their applications
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of dimensional analysis in physics
- Learn how to accurately graph frequency vs. wavelength data
- Explore the concept of definite integrals in relation to physical measurements
- Investigate common sources of error in speed of sound calculations
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, educators, and anyone involved in experimental acoustics or sound measurement who seeks to understand the relationship between frequency and wavelength in calculating the speed of sound.