Haorong Wu
- 419
- 90
- Homework Statement
- Give a quantum circuit to perform the inverse quantum Fourier
- Relevant Equations
- The quantum Fourier transform is defined as ##\left | j \right > =\frac 1 {\sqrt {2^n}} \sum_{j=0}^{2^n-1} e^{2 \pi ijk / 2^n} \left | k \right >##, and it is equal to ##\left | j_1 , j_2 , \dots , j_n \right > \rightarrow \frac { \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2 \pi i 0.j_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2 \pi i 0. j_{n-1} j_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \dots \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2 \pi i 0. j_1 j_2 \dots j_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) } {2^{n/2}}##
First, the inverse quantum Fourier transform is ##\left | k \right > =\frac 1 {\sqrt {2^n}} \sum_{j=0}^{2^n-1} e^{-2 \pi ijk / 2^n} \left | j \right >##, and it is equal to ##\left | k_1 , k_2 , \dots , k_n \right > \rightarrow \frac { \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{-2 \pi i 0.k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{-2 \pi i 0. k_{n-1} k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \dots \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{-2 \pi i 0. k_1 k_2 \dots k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) } {2^{n/2}}##
where I merely change the signs in the exponentials.
Second, since the quantum circuits are reversible, then I think if I reverse the quantum Fourier transform circuit, then I should have the circuit for the inverse quantum Fourier transform as I did in the picture:
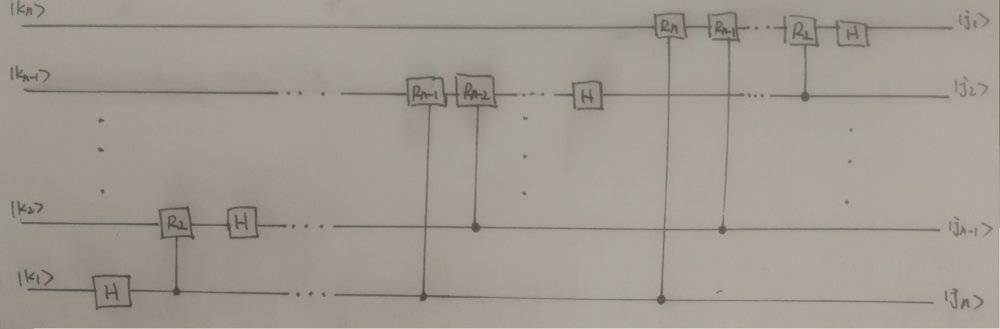
Then, I tried to calculate the outcome of the circuit:
## \left | k_n \dots k_1 \right > \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_2 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_3 \right > \frac {\left | k_2 , 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left |k_2, 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} =\left | k_n \dots k_2 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_3 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \dots \\ \rightarrow \frac { \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0. k_{n-1} k_n } \left | 1 \right > \right ) \dots \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2 \dots k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) } {2^{n/2}}##
which does not match the previous equation. The signs in the exponentials are positive instead of negative.
I think there may be some possible mistakes:
1. I got the wrong inverse quantum Fourier transform, or
2. though quantum circuits are reversible, merely reversing the circuit of quantum Fourier transform will not yield the proper circuit for inverse quantum Fourier transform, or
3. (most probably) I miscalculate the changes in the circuits.
Also, I know that Hadamard gate can be expressed as ## \left | k \right > \rightarrow \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2 \pi i 0.k} \left | 1 \right > } {\sqrt 2} = \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{-2 \pi i 0.k} \left | 1 \right > } {\sqrt 2}## where the negative sign appears in the exponential. Then how can I get other negative signs out? Should I change ##R_k=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{2 \pi i/2^k} \end{pmatrix} ## to ##R_k=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{-2 \pi i/2^k} \end{pmatrix} ##? If so, I believe the origin circuit is right for the inverse quantum Fourier transform.
Thanks!
where I merely change the signs in the exponentials.
Second, since the quantum circuits are reversible, then I think if I reverse the quantum Fourier transform circuit, then I should have the circuit for the inverse quantum Fourier transform as I did in the picture:
Then, I tried to calculate the outcome of the circuit:
## \left | k_n \dots k_1 \right > \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_2 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_3 \right > \frac {\left | k_2 , 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left |k_2, 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} =\left | k_n \dots k_2 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \rightarrow \left | k_n \dots k_3 \right > \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2} \left | 1 \right >} {\sqrt 2} \\ \dots \\ \rightarrow \frac { \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0. k_{n-1} k_n } \left | 1 \right > \right ) \dots \left ( \left | 0 \right > + e^{2\pi i 0.k_1 k_2 \dots k_n} \left | 1 \right > \right ) } {2^{n/2}}##
which does not match the previous equation. The signs in the exponentials are positive instead of negative.
I think there may be some possible mistakes:
1. I got the wrong inverse quantum Fourier transform, or
2. though quantum circuits are reversible, merely reversing the circuit of quantum Fourier transform will not yield the proper circuit for inverse quantum Fourier transform, or
3. (most probably) I miscalculate the changes in the circuits.
Also, I know that Hadamard gate can be expressed as ## \left | k \right > \rightarrow \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{2 \pi i 0.k} \left | 1 \right > } {\sqrt 2} = \frac {\left | 0 \right > + e^{-2 \pi i 0.k} \left | 1 \right > } {\sqrt 2}## where the negative sign appears in the exponential. Then how can I get other negative signs out? Should I change ##R_k=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{2 \pi i/2^k} \end{pmatrix} ## to ##R_k=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{-2 \pi i/2^k} \end{pmatrix} ##? If so, I believe the origin circuit is right for the inverse quantum Fourier transform.
Thanks!