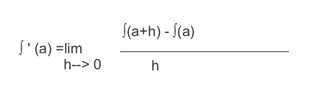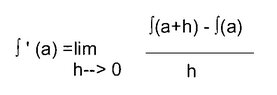jedson303
- 11
- 0
Here's a question. This formula seems to be the keystone of calculus.
View attachment 644That seems to be what the calculus books say, and it makes sense to me, as a rank beginner. This equation is what makes the seeming magic of defining the slope of a dimensionless point on a curved slope possible. And doing that seems to be the major hurdle to opening up things for a calculus. But almost immediatly we are taught to make derivatives by a totally different method -- reducing the exponant by one, etc. So that, for exmple 2x^3 becomes 6x^2 etc. Well, that is of course lots easier. But where is the connection? How does one get from that magical limits equation (which shows how it really does work) to the the cheap trick? (Not that I am necessarily against cheap tricks.)
View attachment 644That seems to be what the calculus books say, and it makes sense to me, as a rank beginner. This equation is what makes the seeming magic of defining the slope of a dimensionless point on a curved slope possible. And doing that seems to be the major hurdle to opening up things for a calculus. But almost immediatly we are taught to make derivatives by a totally different method -- reducing the exponant by one, etc. So that, for exmple 2x^3 becomes 6x^2 etc. Well, that is of course lots easier. But where is the connection? How does one get from that magical limits equation (which shows how it really does work) to the the cheap trick? (Not that I am necessarily against cheap tricks.)