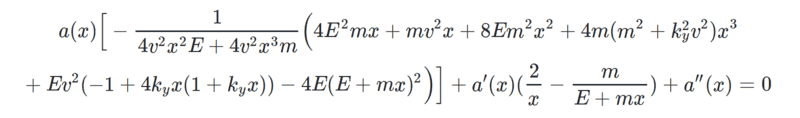Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the transformation of a linear second order ordinary differential equation (ODE) into a hypergeometric function form. Participants explore the identification of singular points and the necessary transformations to achieve this goal, with a focus on the implications of regular and irregular singular points.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant asserts that any linear second order ODE with at most three regular singular points can be transformed into a hypergeometric function.
- Another participant identifies potential singular points at ##x=0## and ##x=-\frac{E}{m}##, and questions the nature of the singularity at ##x=\infty##.
- A participant notes that while ##x=\infty## is a singular point, it is not regular, raising concerns about its applicability in the transformation process.
- One participant provides the form of the hypergeometric equation and suggests transforming the singular points of the original equation to match those of the hypergeometric equation.
- Another participant expresses skepticism about the ability to match the original equation to the hypergeometric form due to the irregular singular point at ##x=\infty##.
- A participant presents a derived equation after attempting the suggested transformation, indicating it does not match the expected hypergeometric form.
- One participant questions the consistency of units in the derived equation, suggesting a re-evaluation of the transformation process.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the feasibility of transforming the given ODE into hypergeometric form, particularly concerning the implications of the irregular singular point at ##x=\infty##. The discussion remains unresolved, with no consensus on the transformation's success.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the importance of identifying singular points accurately and the potential complications arising from irregular singularities. There is an acknowledgment of the need for careful transformations and simplifications, but specific limitations in the original equation's structure are not fully addressed.