Discussion Overview
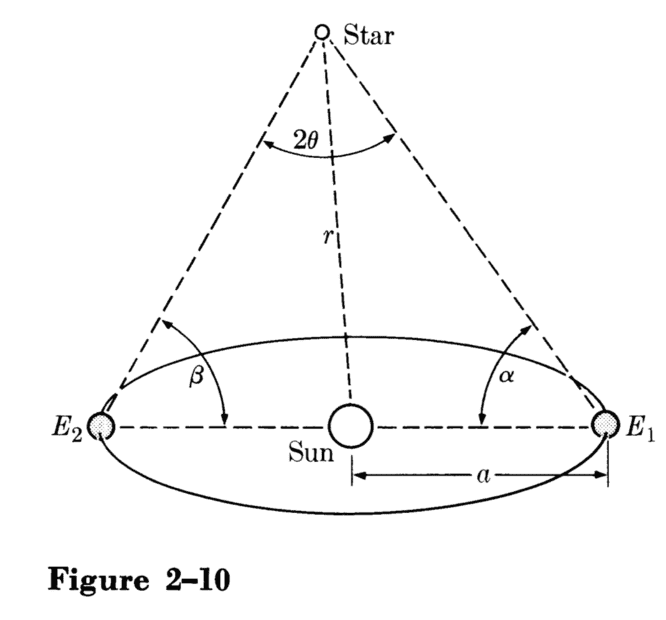
The discussion revolves around the definition of stellar parallax as presented in Alonso and Finn Volume 1. Participants are examining the clarity and interpretation of the definition, particularly regarding the angle described in relation to the Earth's diameter and its orbit.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about the definition of stellar parallax, questioning whether there is a typo or misunderstanding regarding the description provided in the text.
- Another participant asserts that a definition is not derived and suggests that the original poster clarify their concern.
- A later reply seeks to clarify the meaning of the angle theta in the definition, specifically whether it refers to the angle subtended by the Earth's diameter or the diameter of its orbit.
- One participant proposes that the definition likely refers to the Earth's orbit's diameter, arguing that the Earth's diameter itself does not make sense in the context of parallax, which is influenced by the Earth's orbit.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the interpretation of the definition. There are competing views regarding whether the angle refers to the Earth's diameter or its orbital diameter.
Contextual Notes
Participants express uncertainty about the specific terms used in the definition and how they relate to the concept of stellar parallax, indicating potential ambiguities in the text.