Marco Oliveira
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
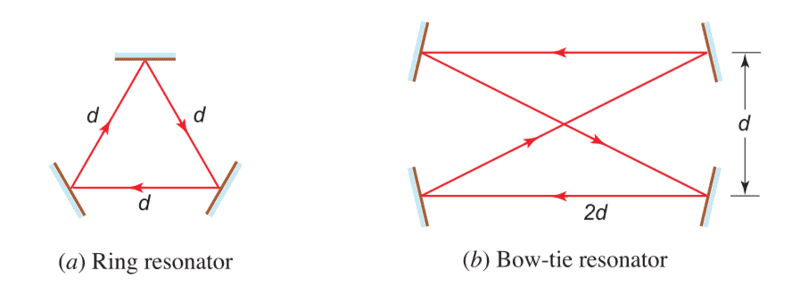
- Derive expressions for the resonance frequencies and their frequency spacing for the three-mirror ring and the four-mirror ring bow-tie resonator shown below. Assume that each mirror reflection introduces a phase shift of π.
- Relevant Equations
- Resonator
I was trying to do the exercise from Saleh's book, but I had some doubts. Any tips on how to resolve it?
My partial solution for the three-mirror ring:
For constructive interference to occur, the total phase accumulated in a round trip must be an integer multiple of 2π. Let's denote the phase accumulated in each arm as ϕ. We have: ϕ + ϕ + ϕ = 2πn, where n is an integer representing the mode number. Since ϕ = π, then: 3π=2πn.
Now i don't know what to do.
My partial solution for the three-mirror ring:
For constructive interference to occur, the total phase accumulated in a round trip must be an integer multiple of 2π. Let's denote the phase accumulated in each arm as ϕ. We have: ϕ + ϕ + ϕ = 2πn, where n is an integer representing the mode number. Since ϕ = π, then: 3π=2πn.
Now i don't know what to do.