Discussion Overview
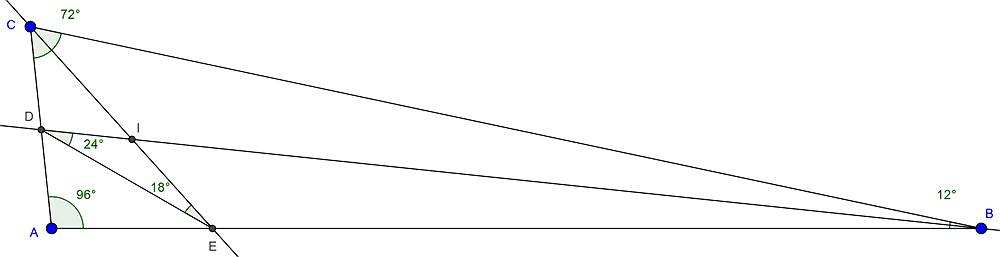
The discussion revolves around calculating the difference in degrees between the measures of the two smallest angles in triangle ABC, given specific angle measures and the use of angle bisectors. The scope includes mathematical reasoning and problem-solving without reliance on software tools like Geogebra.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning, Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- One participant states the known angles BDE and CED are 24 and 18 degrees, respectively, and provides the measure of angle CAB as 96 degrees.
- Another participant recalls that the angles in a triangle sum to 180 degrees and suggests using inspection to determine the angles in the triangle.
- A participant asks how to calculate angle ABC specifically.
- Multiple participants express uncertainty about solving the problem without Geogebra and inquire about the application of the angle bisector theorem.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on how to solve the problem without Geogebra, and there are multiple inquiries about the use of the angle bisector theorem, indicating uncertainty and a lack of agreement on the approach.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the discussion regarding the assumptions made about angle measures and the reliance on visual aids or external resources for problem-solving.