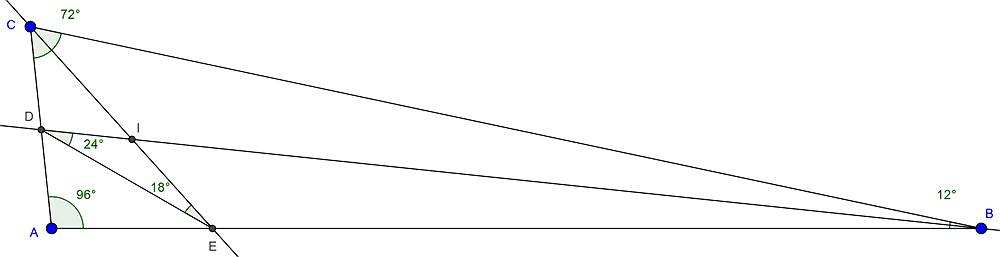
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on calculating the difference between the two smallest angles in triangle ABC, where angle CAB measures 96 degrees, and angles BDE and CED measure 24 and 18 degrees, respectively. Utilizing the properties of angle bisectors and the fact that the sum of angles in a triangle equals 180 degrees, participants derive that angle EID is 138 degrees. The angle bisector theorem is referenced as a potential method for further calculations, emphasizing the importance of understanding angle relationships in triangle geometry.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of triangle properties, specifically the sum of angles in a triangle.
- Familiarity with angle bisectors and their properties.
- Basic knowledge of Euclidean geometry.
- Ability to perform angle calculations and deductions.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Angle Bisector Theorem in detail.
- Practice solving triangle angle problems using Geogebra.
- Learn how to apply the Law of Sines in triangle calculations.
- Explore advanced triangle properties, including the relationship between angles and side lengths.
USEFUL FOR
Students of geometry, mathematics educators, and anyone interested in solving triangle-related problems without relying on software tools like Geogebra.