ebangosh
- 2
- 0
Hi all,
I am a bit new in this, am trying to learn DE, dynamical systems, & chaos. I am looking into some answers for the following questions:
1) Is it always possible to derive a difference equation for every differential equation, and if so how do we do that?
2) Consider Lorenz system:
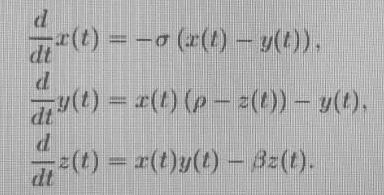
Where does Lorenz map/discrete version coming from, was it derived from Lorenz system?
3) I heard about Baker's map but I couldn't figure if Baker's map was also derived from a system of linear differential equation too?
4) If the original system of differential eqns exhibits chaotic characteristic, will this characteristic remains in difference equation?
Thanks for your helps.
I am a bit new in this, am trying to learn DE, dynamical systems, & chaos. I am looking into some answers for the following questions:
1) Is it always possible to derive a difference equation for every differential equation, and if so how do we do that?
2) Consider Lorenz system:
Where does Lorenz map/discrete version coming from, was it derived from Lorenz system?
3) I heard about Baker's map but I couldn't figure if Baker's map was also derived from a system of linear differential equation too?
4) If the original system of differential eqns exhibits chaotic characteristic, will this characteristic remains in difference equation?
Thanks for your helps.