SUMMARY
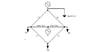
The discussion focuses on calculating power flux distribution in a schematic involving S (load) and G (generator) components. Participants clarify that the task requires determining the power carried in six transmission lines, with specific attention to the labeling of lengths, particularly L5 and L6. The conversation highlights the importance of accurate labeling in schematic diagrams to avoid confusion and ensure correct calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electrical schematic symbols, specifically S for load and G for generator.
- Familiarity with power distribution concepts in electrical engineering.
- Knowledge of transmission line theory and its application in circuit analysis.
- Ability to interpret and analyze schematic diagrams accurately.
NEXT STEPS
- Research power flow analysis techniques in electrical circuits.
- Study the principles of transmission line modeling and calculations.
- Learn about common errors in schematic interpretation and how to avoid them.
- Explore software tools for simulating power distribution in electrical networks.
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and professionals involved in power distribution analysis will benefit from this discussion.