SUMMARY
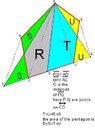
The discussion focuses on dividing a convex pentagon ABCDE into two equal-area parts by constructing a line through point A. For a regular pentagon, the midpoint of segment CD, denoted as F, can be used to draw line AF, effectively splitting the pentagon. The conversation references Albert's solution, which involves finding the midpoint M of segment PQ and drawing line AM, contingent on M being positioned between points C and D. However, the participants highlight that this condition may not always hold true, indicating the need for further exploration of the geometric properties involved.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of convex polygons, specifically pentagons.
- Knowledge of geometric constructions, including midpoints and line segments.
- Familiarity with area calculations in polygons.
- Basic principles of geometric proofs and visual representations.
NEXT STEPS
- Study geometric constructions involving midpoints in polygons.
- Learn about area division techniques in irregular shapes.
- Explore geometric proof strategies, including "proof without words".
- Investigate the properties of convex polygons and their area relationships.
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, geometry students, and educators interested in polygon properties and area division techniques will benefit from this discussion.