mathmari
Gold Member
MHB
- 4,984
- 7
Hey! 
I want to draw a circuit that has four inputs a, b, c, d, and which gives the value $[(a \lor b) \lor (c \lor \neg d)] \land (c \land \neg a)$ at the output, using exclusively the NAND gates with two inputs.
Hint: If you connect the two inputs of such a NAND gate, you get a so-called inverter, i.e. a circuit implementation of the logical negation.
The NAND-gate is:
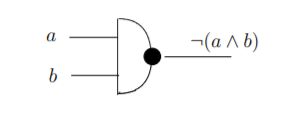
I have done the following:
\begin{align*}[(a\lor b)\lor (c\lor \neg d)]\land (c\land \neg a)&=[\neg (\neg a\land \neg b)\lor \neg (\neg c\land d)]\land (c\land \neg a)\\ & =\neg [(\neg a\land \neg b)\land (\neg c\land d)]\land (c\land \neg a)\end{align*}
We can get the part $\neg [(\neg a\land \neg b)\land (\neg c\land d)]$ using the NAND gate, right? What about the second part? Do we have to write it in an other way? :unsure:
I want to draw a circuit that has four inputs a, b, c, d, and which gives the value $[(a \lor b) \lor (c \lor \neg d)] \land (c \land \neg a)$ at the output, using exclusively the NAND gates with two inputs.
Hint: If you connect the two inputs of such a NAND gate, you get a so-called inverter, i.e. a circuit implementation of the logical negation.
The NAND-gate is:
I have done the following:
\begin{align*}[(a\lor b)\lor (c\lor \neg d)]\land (c\land \neg a)&=[\neg (\neg a\land \neg b)\lor \neg (\neg c\land d)]\land (c\land \neg a)\\ & =\neg [(\neg a\land \neg b)\land (\neg c\land d)]\land (c\land \neg a)\end{align*}
We can get the part $\neg [(\neg a\land \neg b)\land (\neg c\land d)]$ using the NAND gate, right? What about the second part? Do we have to write it in an other way? :unsure: