FlipStyle1308
- 264
- 0
Problem:
A given system has the equipotential surfaces shown below, where Vo = 12.0 V.
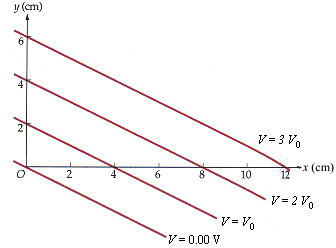
(a) What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field?
(b) What is the shortest distance one can move to undergo a change in potential of 5.00 V?
I am not too sure on what equations I can use to solve this, but I have a feeling one of them will be delta V = -W/qo, and I have no other ideas on how to approach this problem.
A given system has the equipotential surfaces shown below, where Vo = 12.0 V.
(a) What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field?
(b) What is the shortest distance one can move to undergo a change in potential of 5.00 V?
I am not too sure on what equations I can use to solve this, but I have a feeling one of them will be delta V = -W/qo, and I have no other ideas on how to approach this problem.