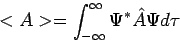Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the calculation of expectation values in quantum mechanics, specifically using a linear combination of wavefunctions and an operator. Participants explore the mathematical steps involved in substituting wavefunctions into the integral for expectation values, addressing LaTeX formatting issues and clarifying notation.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- One participant requests a step-by-step guide for calculating expectation values using a specific wavefunction and operator.
- Another participant suggests substituting the entire wavefunction and its conjugate into the integral without multiplying out the products initially.
- There are discussions about the correct representation of subscripts in LaTeX and how to format equations properly.
- Participants clarify that the expectation value can be expressed as an integral involving the wavefunctions and the operator.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of using different indices for summation to avoid confusion.
- Another participant notes the elegance of using the absolute value of complex conjugates in the calculations.
- There is a discussion about the representation of eigenvalues associated with the operator and their relation to the wavefunctions.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the steps to calculate expectation values, but there are variations in notation and some uncertainty regarding the simplification of expressions. The discussion remains unresolved on certain aspects of the mathematical steps and notation.
Contextual Notes
Participants express confusion over specific mathematical steps and LaTeX formatting, indicating that some assumptions about notation and simplification may not be universally understood.