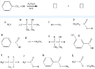
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on identifying the products of a chemical reaction involving alcohol and Potassium Dichromate. The user initially believed the product was only K, but further clarification revealed that the reaction produces a carboxylic acid, specifically represented by the letter E. Potassium Dichromate acts as an oxidizing agent in the presence of hydrochloric acid, facilitating the oxidation of alcohol to form the carboxylic acid characterized by the COOH functional group.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of organic chemistry reactions
- Knowledge of oxidizing agents, specifically Potassium Dichromate
- Familiarity with functional groups, particularly carboxylic acids
- Basic knowledge of reaction mechanisms involving alcohols
NEXT STEPS
- Research the mechanism of alcohol oxidation by Potassium Dichromate
- Study the properties and reactions of carboxylic acids
- Explore the role of acidic conditions in oxidation reactions
- Learn about other common oxidizing agents used in organic chemistry
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, organic chemists, and anyone involved in reaction mechanism studies will benefit from this discussion.