Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the probability that a randomly selected child receives both a toffee and a chocolate from a group of 35 students. Participants explore different interpretations of the problem, focusing on the implications of selection order and the nature of probability in this context.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
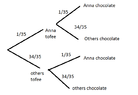
- Some participants propose that the probability of a child receiving both candies could be calculated as $\frac{1}{35} + \frac{1}{35} = \frac{2}{35}$, while others question whether it should be $\frac{1}{35} * \frac{1}{35}$.
- One participant suggests that if a specific child (e.g., Anna) receives the toffee, the probability that she also receives the chocolate is $\frac{1}{35}$, leading to a combined probability of $\frac{1}{1225}$ if calculated multiplicatively.
- Another participant argues that the chance of any one student receiving both candies is simply $\frac{1}{35}$, emphasizing that it does not depend on which student is selected first.
- There is a discussion about whether the events are mutually exclusive and how the rules of probability apply in this scenario.
- One participant clarifies that if a specific student is considered before the selection of candies, the probability would be the square of $\frac{1}{35}$, but in this case, the selection occurs after the first candy is given.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on how to calculate the probability, with no consensus reached on the correct approach. Some support the idea that the probability is $\frac{1}{35}$, while others present alternative calculations and interpretations.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the importance of selection order and the implications of defining the problem, which may affect the interpretation of probabilities involved.