SUMMARY
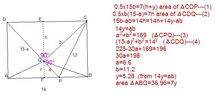
The area of triangle ABQ within rectangle ABCD can be calculated using the given dimensions: AB = 14, CP = 13, and DP = 15. Point P lies on line segment AB, while point Q is positioned on line segment DP, with line segment CQ perpendicular to DP at point Q. The area of triangle ABQ is determined to be 84 square units through the formula for the area of a triangle, A = 0.5 * base * height, where the base is AB and the height is the vertical distance from Q to line AB.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic geometry concepts, specifically triangles and rectangles.
- Familiarity with the properties of perpendicular lines.
- Knowledge of area calculation formulas for triangles.
- Ability to visualize geometric figures based on given points and lengths.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of triangles and rectangles in Euclidean geometry.
- Learn how to apply the Pythagorean theorem in geometric problems.
- Explore advanced area calculation techniques for irregular shapes.
- Investigate coordinate geometry to enhance understanding of points and lines in a plane.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying geometry, educators teaching geometric principles, and anyone interested in solving geometric problems involving areas and dimensions.