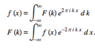SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the application of the Fourier transform to calculate the power of a signal. It clarifies that the function f(x) in the context of Fourier transforms represents the original signal x(t), not its power. The Fourier transform, denoted as X(f) or X_n, is utilized to analyze the frequency components of the signal, and it is essential to take the absolute value of the result after performing the Fourier transform to obtain meaningful power information.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Fourier transform principles
- Familiarity with signal representation (x(t))
- Knowledge of frequency domain analysis
- Basic concepts of power in electrical signals
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of the Fourier transform in signal processing
- Learn how to compute the power spectral density of a signal
- Explore the relationship between time-domain and frequency-domain representations
- Investigate the implications of taking the absolute value in Fourier analysis
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, signal processing students, and anyone involved in analyzing power signals using Fourier transforms will benefit from this discussion.