Tibo123
- 6
- 0
Hello,
My name is Thibaut. I am looking to improve my code in python in order to have a better look a my Fourier transform. as you can see on the image, we barely see any detail of the peaks on the image. Also it's not centred. the zero order peak in on the corner, not in the centre.
Any idea how to fix it?
Thibaut
image: click here
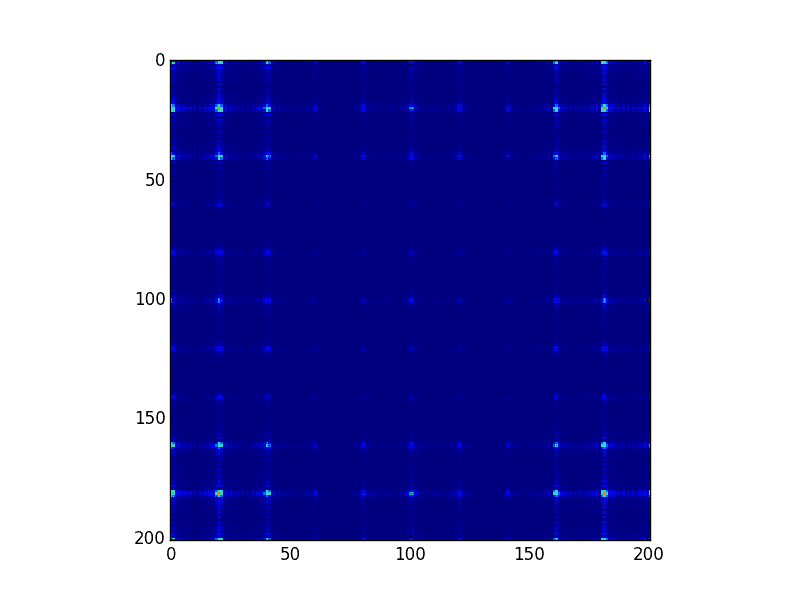
My name is Thibaut. I am looking to improve my code in python in order to have a better look a my Fourier transform. as you can see on the image, we barely see any detail of the peaks on the image. Also it's not centred. the zero order peak in on the corner, not in the centre.
Any idea how to fix it?
Thibaut
image: click here
Python:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.linspace(-100, 100.0, 201.0, endpoint = True)
y = np.linspace(-100, 100.0, 201.0, endpoint = True)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y, sparse=True)
def f1(a,b):
return np.piecewise(a, [abs(a) < 2, abs(a) >= 2], [1, 0]) * np.piecewise(b, [abs(b) < 2, abs(b) >= 2], [1, 0])
def f2(r,c):
spacing=10
a=np.zeros([r,c])
for ii in range (r):
for jj in range(c):
if (ii%spacing)==0 and (jj%spacing)==0 and abs(ii-100)<55 and abs(jj-100)<55:
a[ii,jj]=1
else:
a[ii,jj]=0
return a
h = np.fft.fft2(f1(xx,yy))
g = np.fft.fft2(f2(201,201))
k=abs(h)*abs(g)plt.imshow(np.abs(k),interpolation='nearest')
#plt.imshow(f1(xx,yy),interpolation='nearest')
#plt.imshow(f2(200,200),interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()