- #1
iScience
- 466
- 5
refer to the following image
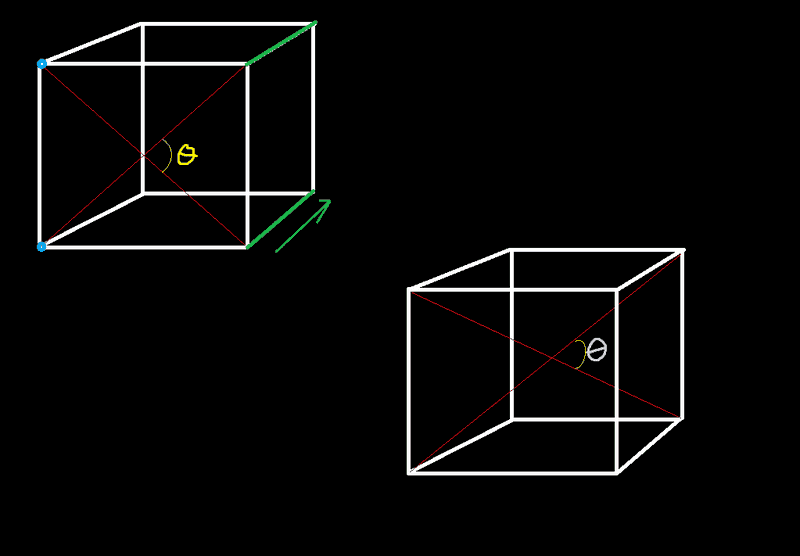
so consider the angle of the yellow theta on the top left. this is 45*. if we fix one side of both red lines at the blue circles, and we slide the other end along the green side of the cube, ie just think of the green lines as rails for the red lines to slide along. then this will extend the lateral length of the lines as the length in the z-direction (up and down) remains constant. shouldn't this then DECREASE the angle specified in the picture not increase it?
i'm asking because I've been asked to solve for this angle and θ<45* is not what i got. I got the angle to be 70* which is not intuitive.
i am asking for intuition on this problem as opposed to an involved analytical method of solving for that angle. I've already done it analytically i just have no idea why that angle increases and doesn't decrease.
thanks all
so consider the angle of the yellow theta on the top left. this is 45*. if we fix one side of both red lines at the blue circles, and we slide the other end along the green side of the cube, ie just think of the green lines as rails for the red lines to slide along. then this will extend the lateral length of the lines as the length in the z-direction (up and down) remains constant. shouldn't this then DECREASE the angle specified in the picture not increase it?
i'm asking because I've been asked to solve for this angle and θ<45* is not what i got. I got the angle to be 70* which is not intuitive.
i am asking for intuition on this problem as opposed to an involved analytical method of solving for that angle. I've already done it analytically i just have no idea why that angle increases and doesn't decrease.
thanks all