karush
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,240
- 5
$\tiny{GRE.al.4}$
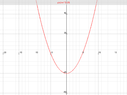
Find the domain of $f(x)=\sqrt{x^2-25}$
a. $[x\le-5]U[x\ge 5]$
b. x=5
c. $5 \le x$
d. $x\ne 5$
e. $\textit{all reals}$
well just by observation because of the radical I chose c.
but was wondering if imaginary numbers could be part of the domain alto it is not asked for here
https://dl.orangedox.com/QS7cBvdKw55RQUbliE
Find the domain of $f(x)=\sqrt{x^2-25}$
a. $[x\le-5]U[x\ge 5]$
b. x=5
c. $5 \le x$
d. $x\ne 5$
e. $\textit{all reals}$
well just by observation because of the radical I chose c.
but was wondering if imaginary numbers could be part of the domain alto it is not asked for here
https://dl.orangedox.com/QS7cBvdKw55RQUbliE