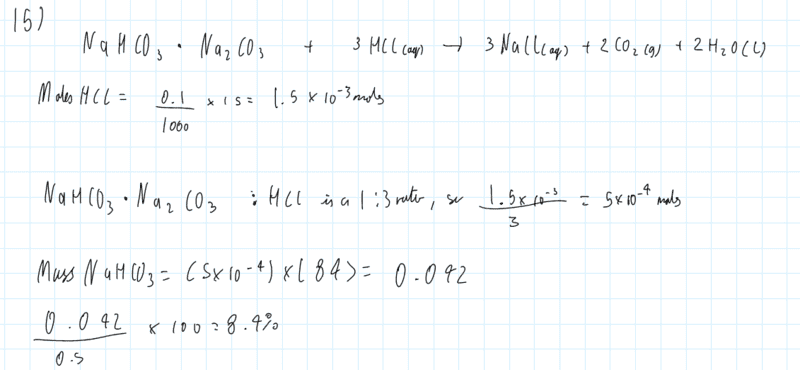Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around a chemistry molar calculation involving sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), focusing on the setup of equations and conversions related to molarity and volume. The scope includes mathematical reasoning and conceptual clarification of the calculations involved.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
- One participant points out that the initial equation assumes equal molar amounts of NaHCO3 and Na2CO3, suggesting this assumption leads to errors in the calculation.
- Another participant proposes setting up two simultaneous equations for the amounts of NaHCO3 (x) and Na2CO3 (y) to solve the problem.
- A participant raises a question about calculating the moles of HCl in a given volume of acid solution, specifically 15 cc.
- One participant attempts to clarify the conversion between decimeters and centimeters, noting a mistake in their earlier calculation regarding the conversion of molarity from dm^3 to cm^3.
- Another participant reiterates the conversion process, providing a corrected calculation for moles per cubic centimeter.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the assumptions made in the initial calculation, and there is no consensus on the correct approach to solving the problem. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the proper setup of equations and the accuracy of the calculations presented.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the assumptions made about the amounts of reactants, and the conversions between different units of volume and concentration are not fully resolved, leading to potential confusion in the calculations.