SUMMARY
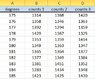
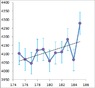
The discussion centers on normalizing a dataset of counts measured at various angles to a maximum of 100. The user has calculated the mean and standard deviation for the counts but is uncertain about the normalization process. Key insights include the importance of avoiding the division of all observations by a single value, as this can distort the dataset, and the necessity of understanding the underlying model, such as a Gaussian curve, for accurate normalization. The conversation highlights the need for clarity on measurement periods and the relationship between counts per second and counts over a specified duration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Gaussian curve fitting
- Knowledge of statistical measures such as mean and standard deviation
- Familiarity with data normalization techniques
- Basic concepts of error analysis in measurements
NEXT STEPS
- Learn about Gaussian curve fitting techniques in data analysis
- Research normalization methods for datasets with varying measurement periods
- Explore error analysis and its impact on data interpretation
- Study the implications of using different statistical measures for data representation
USEFUL FOR
Data analysts, researchers in experimental physics, and anyone involved in statistical data normalization and analysis will benefit from this discussion.