- #1
kanibal
- 2
- 0
Hello
i am working on a small clutch cable testing machine this machine can give the lifetime of clutch cable
i need some assistance to figure out how much forces i need to apply on this mechanism , and because the cable related directly in the clutch I'm asking if the force in the clutch in the same us what we give to the pedal example : if i push the pedal with 200 N how mach force is applied into release the clutch it is the same 200 N or more and why !
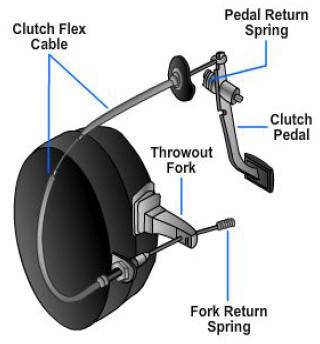
this is the mechanism i made
i am working on a small clutch cable testing machine this machine can give the lifetime of clutch cable
i need some assistance to figure out how much forces i need to apply on this mechanism , and because the cable related directly in the clutch I'm asking if the force in the clutch in the same us what we give to the pedal example : if i push the pedal with 200 N how mach force is applied into release the clutch it is the same 200 N or more and why !
this is the mechanism i made