Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the application of a one-dimensional equation related to electric fields and charge densities. Participants explore the implications of integrating charge density and the resulting electric field configurations in different scenarios, specifically comparing two figures representing these concepts.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
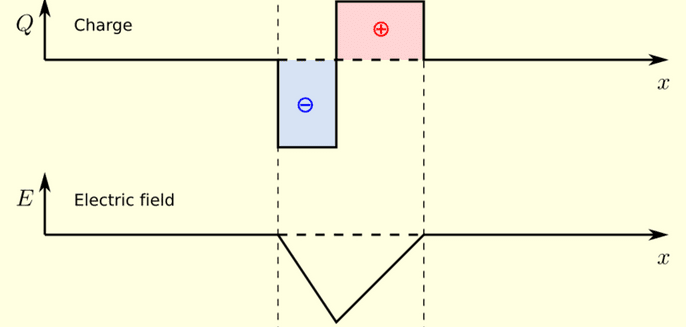
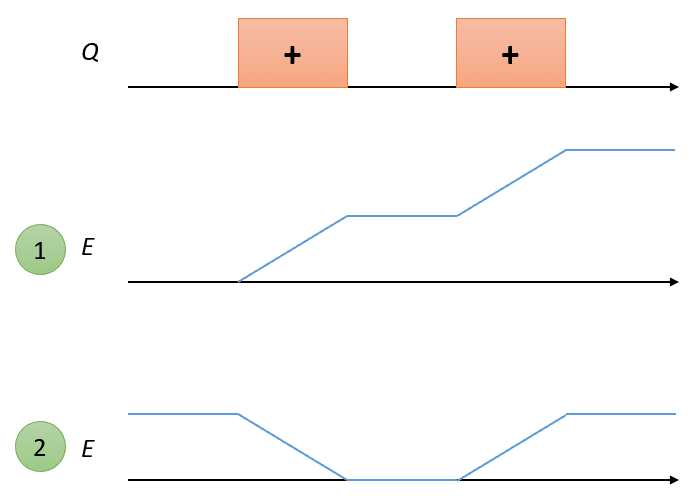
- One participant questions the application of the 1D equation to two figures, suggesting that there should be a field present between the charge densities.
- Another participant asserts that the intuition is incorrect, explaining that the electric fields point in opposite directions and that a negative constant of integration leads to zero electric field between the charges.
- A participant acknowledges a misunderstanding and seeks clarification on the application of the 1D equation.
- Further clarification is provided that the constant of integration must be determined from boundary conditions, indicating that the first graph needs adjustment to resemble the second graph.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is disagreement regarding the initial intuition about the electric field configuration. While some participants provide corrections and clarifications, the overall application of the 1D equation and the implications of the constant of integration remain points of discussion without a clear consensus.
Contextual Notes
Participants discuss the need for boundary conditions in determining the constant of integration, which may not have been fully established in the initial claims. The implications of these conditions on the electric field configurations are not resolved.