MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here is the question:
I have posted a link there to this topic so the OP can see my work.
edit: Unfortunately, the OP deleted the question before I had a chance to post my response there.
Help with cost functions?
Hi there,
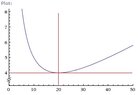
Got this cost function question where C(x) = 40/x + x/10
I need to find x where x=distance in meters between the poles that will minimize the cost.
Thanks for any help/hints!
I have posted a link there to this topic so the OP can see my work.
edit: Unfortunately, the OP deleted the question before I had a chance to post my response there.