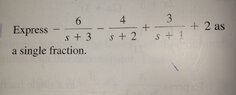Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around solving algebraic fractions, specifically focusing on rewriting a given expression as a single rational expression. Participants explore the steps involved in combining multiple fractions, including determining the lowest common denominator (LCD) and simplifying the expression.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
- One participant requests help in solving an expression involving multiple fractions, indicating uncertainty about starting with three or more sums.
- Another participant provides a detailed breakdown of rewriting the expression $$-\frac{6}{s+3}-\frac{4}{s+2}+\frac{3}{s+1}+2$$ as a single rational expression, emphasizing the importance of finding the LCD and multiplying each term appropriately.
- A third participant expresses satisfaction after working through the calculations, noting the challenge of simplifying the expression fully.
- Another participant suggests that the process is similar to the basic rule of combining two fractions, indicating that those familiar with the method should find it straightforward.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the steps needed to combine the fractions, but there is no explicit consensus on the best approach or the complexity of the calculations involved.
Contextual Notes
Some participants may have varying levels of familiarity with algebraic fractions, which could affect their understanding of the steps discussed. The discussion does not resolve any potential confusion regarding the simplification process.
Who May Find This Useful
Students or individuals seeking assistance with algebraic fractions, particularly those struggling with combining multiple fractions into a single expression.