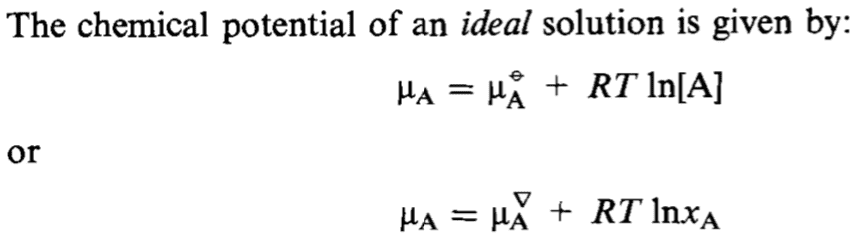SUMMARY
The small triangle symbol (▽) in the context of chemical potential likely represents an outdated notation for the chemical potential of a pure solvent A (μA*). The discussion clarifies that in ideal solutions, where the activity coefficient (γA) equals 1, the chemical potential can be expressed as μA = μA* + RTlnxA. This formulation aligns with the principles of Raoult's Law, indicating that the reference state for the second equation is pure A, while the first equation uses a 1M concentration reference state.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of chemical potential and Gibbs energy
- Familiarity with Raoult's Law and ideal solutions
- Knowledge of mole fraction and activity coefficients
- Basic concepts of vapor pressure in chemistry
NEXT STEPS
- Study the IUPAC recommendations for chemical notation in thermodynamics
- Learn about the derivation of chemical potential in ideal solutions
- Explore the implications of Raoult's Law on vapor pressure and solutions
- Investigate the role of activity coefficients in non-ideal solutions
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, researchers in physical chemistry, and professionals working with thermodynamic properties of solutions will benefit from this discussion.