- #1
Eggue
- 13
- 2
- Homework Statement
- A heavy horizontal girder of length L has several objects suspended from it. It is supported by a frictionless pivot at its left end and a cable of negligible weight that is attached to an I-beam at a point a distance h directly above the girder’s center. Where should the other end of the cable be attached to the girder so that the cable’s tension is a minimum?
- Relevant Equations
- Conditions for equilibrium
I honestly have no idea where I'm going wrong
i've checked my differentiation using a derivative calculator but the answer is the same.
The answer from the book is [itex]\frac{L}{2} + \frac{h^2}{L}[/itex]
Working:
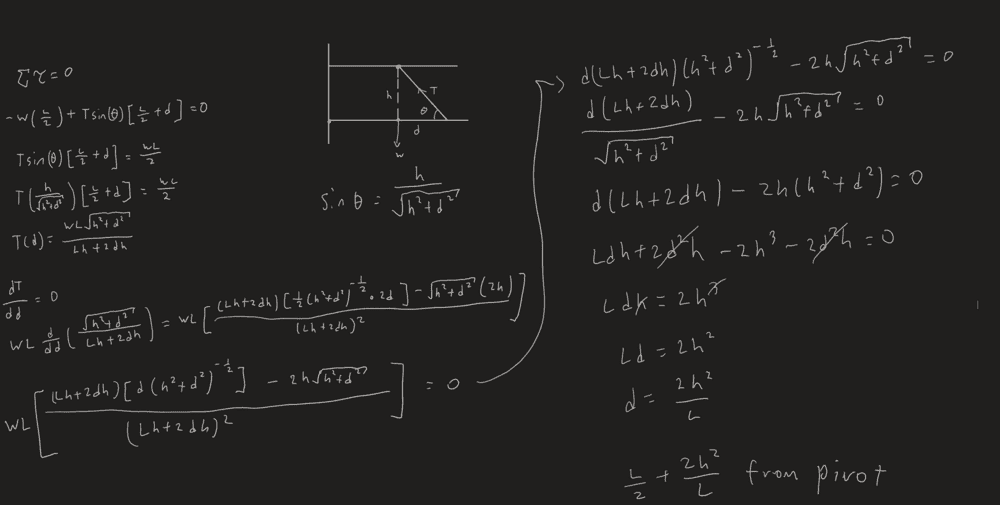
i've checked my differentiation using a derivative calculator but the answer is the same.
The answer from the book is [itex]\frac{L}{2} + \frac{h^2}{L}[/itex]
Working: