- 2,180
- 2,691
Have a look at the article here.
From the article:
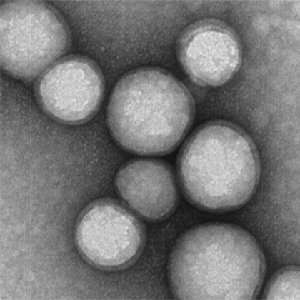
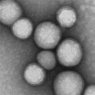
Transmission electron microscopy of neutrophil nanosponges. Credit: Qiangzhe Zhang/Nature Nanotechnology
From the article:
Neutrophils are among the immune system's first responders against invading pathogens. They are also known to play a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease that causes painful inflammation in the joints and can ultimately lead to damage of cartilage and bone tissue.
When rheumatoid arthritis develops, cells in the joints produce inflammatory proteins called cytokines. Release of cytokines signals neutrophils to enter the joints. Once there, cytokines bind to receptors on the neutrophil surfaces, activating them to release more cytokines, which in turn draws more neutrophils to the joints and so on.
The nanosponges essentially nip this inflammatory cascade in the bud. By acting as tiny neutrophil decoys, they intercept cytokines and stop them from signaling even more neutrophils to the joints, reducing inflammation and joint damage.
Transmission electron microscopy of neutrophil nanosponges. Credit: Qiangzhe Zhang/Nature Nanotechnology