evinda
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,741
- 0
Hello! (Wave)
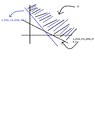
There is given the following example of a linear programming problem that has no optimal solution.
View attachment 4813
$$\begin{Bmatrix}
a_{11}x_1+a_{12}x_2 \geq b_1 & \\
a_{21}x_1+a_{22}x_2 \geq b_2 &
\end{Bmatrix} \Leftrightarrow (x_1,x_2) \in D \\ \\ \\ \\ \ \ \max_{(x_1, x_2) \in D} (x_1+x_2)$$
How could we explain formally that there is no optimal solution? (Thinking)
There is given the following example of a linear programming problem that has no optimal solution.
View attachment 4813
$$\begin{Bmatrix}
a_{11}x_1+a_{12}x_2 \geq b_1 & \\
a_{21}x_1+a_{22}x_2 \geq b_2 &
\end{Bmatrix} \Leftrightarrow (x_1,x_2) \in D \\ \\ \\ \\ \ \ \max_{(x_1, x_2) \in D} (x_1+x_2)$$
How could we explain formally that there is no optimal solution? (Thinking)