CloudNine
- 15
- 3
Hi all,
I got an exercise to plot Bethe-Bloch function (ignore the "Compare..." part, it belongs to an exercise above), for alpha particle in Xenon. See the question below:
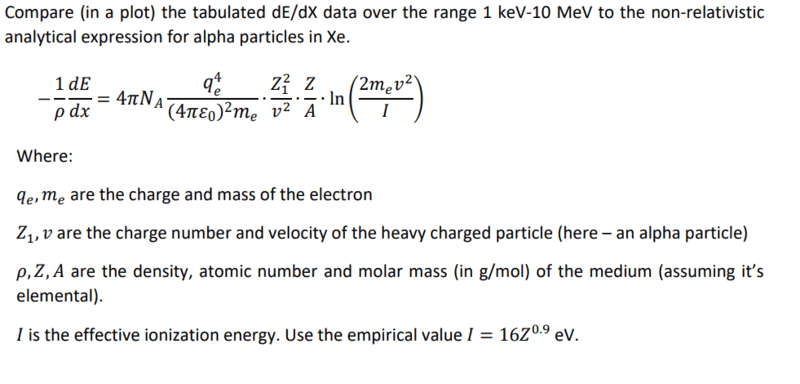
I've been struggling to get a plot that makes sense. I checked my parameters and the units a million times already, but couldn't find where the problem is. On paper, the units I'm left with, after all the conversions, are MeV/cm, which is exactly what I want. But again, I get a weird curve...
Here is the Matlab code I wrote:
I know that the peak shouldn't be that sharp, narrow, high (10^4!) and not that close to zero. Also, the dE/dx trend should be more moderate and to spread much more nicely, than this sharp drop to 0..
Would appreciate your thoughts!
Thanks.
I got an exercise to plot Bethe-Bloch function (ignore the "Compare..." part, it belongs to an exercise above), for alpha particle in Xenon. See the question below:
I've been struggling to get a plot that makes sense. I checked my parameters and the units a million times already, but couldn't find where the problem is. On paper, the units I'm left with, after all the conversions, are MeV/cm, which is exactly what I want. But again, I get a weird curve...
Here is the Matlab code I wrote:
Code:
E_dat=[ 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.003 0.004 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.009 0.010 0.013 0.015 0.018 0.020 0.023 0.025 0.028 0.030 0.035 0.040 0.045 0.050 0.055 0.060 0.065 0.070 0.075 0.080 0.085 0.090 0.095 0.100 0.125 0.150 0.175 0.200 0.225 0.250 0.275 0.300 0.350 0.400 0.450 0.500 0.550 0.600 0.650 0.700 0.750 0.800 0.850 0.900 0.950 1.000 1.250 1.500 1.750 2.000 2.250 2.500 2.750 3.000 3.500 4.000 4.500 5.000 5.500 5.544 6.000 6.500 7.000 7.500 8.000 8.500 9.000 9.500 10.000 ];%MeV
% Constants for Bethe-Bloch equation:
rho = 0.010592; % [g/cm^3] for Xenon in 2 bar and 25 C conditions
qe=1.602e-19; % C
me=9.109e-28; % g
NA=6.0226e23; % Avogadro constant, 1/mol
K=9e13; % K=1/4*pi*epsilon0 , units of N*cm^2/C^2
Z1=2;
malpha=6.646e-24; % g
v=sqrt(2*E_dat/malpha); % sqrt(MeV/g)
A=131.293; % g/mol
Z=54;
I=(16*Z^0.9)/1e6; % MeV
first=-rho*4*pi*NA;
second=((qe^4)*(K^2))/me;
third=((Z1^2)./(v.^2));
fourth=Z/A;
fifth=log((2*me*(v.^2))./I);
aaa=first*second*fourth;
bbb=third.*fifth;
dEdX_BB=aaa*bbb*3.9e21; % 3.9e21 is to convert from N^2*cm/MeV to MeV/cm
plot(E_dat,dEdX_BB)
xlabel('Alpha energy [MeV]')
ylabel('dE/dX [MeV/cm]')
title('Stopping power of non-relativistic analytical expression for alpha particle Xe')I know that the peak shouldn't be that sharp, narrow, high (10^4!) and not that close to zero. Also, the dE/dx trend should be more moderate and to spread much more nicely, than this sharp drop to 0..
Would appreciate your thoughts!
Thanks.
Last edited: