MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
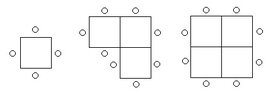
We wish to find how many people can be seated around a table. We may form larger tables by pushing together smaller square tables and arranging people as shown in the diagram:
View attachment 1261
There are two rules we are required to follow when pushing the smaller tables together and arranging the people around the larger table:
Determine:
a) The number of people that may be seated for a given number of smaller tables.
b) The minimum number of smaller tables required to seat a given number of people.
View attachment 1261
There are two rules we are required to follow when pushing the smaller tables together and arranging the people around the larger table:
- Only 1 person may be seated at one side of a smaller table
- The larger table must be made as square as possible
Determine:
a) The number of people that may be seated for a given number of smaller tables.
b) The minimum number of smaller tables required to seat a given number of people.