Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around evaluating the triple integral of the function \(x^2 e^y\) over a volume \(E\) defined by a parabolic cylinder and several planes. Participants explore the appropriate order of integration and the implications of the limits set by the geometry of the region.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
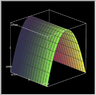
- Participants discuss the integral \(I=\iiint\limits_{E} x^2 e^y dV\) and the boundaries defined by the parabolic cylinder \(z=1-y^2\) and the planes \(z=0\), \(x=1\), and \(x=-1\).
- Some participants suggest different orders of integration and question which would be most effective for evaluating the integral.
- There is a concern raised about the limits of integration for \(z\) being dependent on \(y\), indicating that the integral would yield a function of \(y\) rather than a numeric result.
- One participant points out that the parabolic cylinder does not bound a finite region and questions whether the evaluation should be restricted to the first octant.
- A later reply suggests an alternative order of integration and encourages the exploration of symmetries that could simplify the integral.
- Another participant introduces a related follow-up question involving a formula for the difference of integrals \(I_n(1)-I_n(-1)\) and provides a verification step for a related integral involving \(e^x\).
- Participants inquire about the graphing tools used to visualize the volume in question.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the appropriate order of integration and the implications of the limits. There is no consensus on the best approach to evaluating the integral, and the discussion remains unresolved regarding the boundaries and their implications.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations regarding the assumptions about the bounded region, particularly concerning whether the evaluation should be confined to the first octant. The discussion also highlights the dependence of integration limits on the variables involved.
Who May Find This Useful
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those focusing on multivariable calculus and integration techniques, may find this discussion relevant.